
ตัวอย่างนี้เป็นตัวอย่างที่อ่านและทดลองทำจากบทความต้นฉบับนี้ Serving Web Content with Spring MVC โดยใช้เครื่องมือคือ Spring Tool Suite
Stack
- ระบบปฎิบัติการที่ใช้ : Ubuntu 14.04
- เครื่องมือ : Spring Tool Suite 3.6.3
- Java JDK 7 update 65 (1.7.0_65)
- เวลาที่ใช้ : ประมาณ 45 นาที (รวมการอ่าน ทำความเข้าใจด้วย)
สร้างโปรเจ็ค
เปิด Spring Tool Suite ขึ้นมา จากนั้นทำการ Import โปรเจ็ค โดยค้นหา “Serving web content”
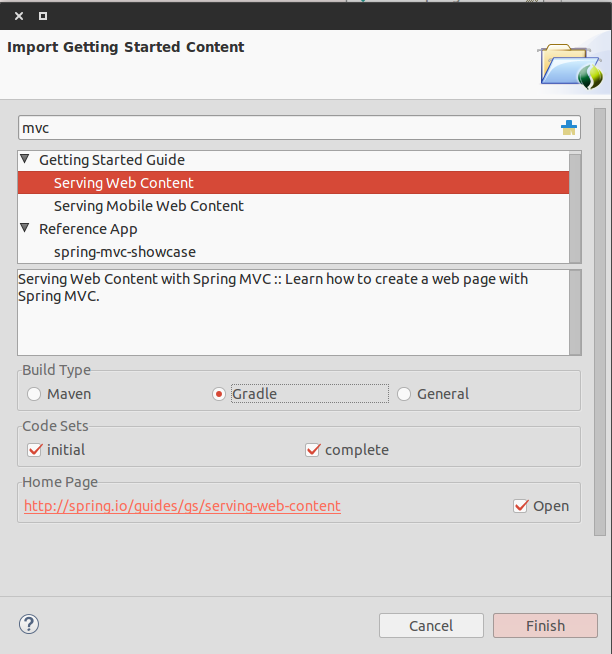
- Build Type : เลือกเป็น Gradle
เมื่อ Import ได้แล้ว จะเห็นโปรเจ็คอยู่สองตัว คือ
- gs-serving-web-content-initial
- gs-serving-web-content-complete
ตัว gs-serving-web-content-initial เป็นโปรเจ็คเปล่าๆ เราจะใช้ตัวนี้ ส่วนอีกตัว gs-serving-web-content-complete เป็นโปรเจ็คที่เสร็จแล้ว เผื่อเอาไว้ดูเปรียบเทียบว่าเราทำตรงไหนผิดพลาด
สร้าง Web Controller
ใน Spring, ตัว Controller จะเป็นตัวควบคุม HTTP request ต่างๆ ง่ายๆ โดยการใส่ annotation @Controller อย่างเช่น ตัวอย่าง GreetingController เป็นตัวจัดการ GET สำหรับ /greeting โดย return เป็น ชื่อของ View กลับมาเพื่อทำการ render เป็น HTML
ไฟล์ /src/main/java/hello/GreetingController.java
package hello;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controllerpublic class GreetingController {
@RequestMapping("/greeting") public String greeting( @RequestParam(value="name", required=false, defaultValue="world") String name, Model model) { model.addAttribute("name", name); return "greeting"; }}@RequestMapping: เป็น annotation สำหรับ mapping ระหว่าง HTTP request/greetingกับเมธอดgreeting()@RequestParam: จะทำการ bind ค่าจาก query String parameternameเข้ากับ parameternameของเมธอดgreeting()โดย query String parameter เซตค่าrequiredเป็น false คือไม่บังคับว่าจะต้องมีหรือไม่มีก็ได้ ถ้าไม่มีก็จะใช้ค่าdefaultValueแทน โดยค่าของnameก็จะถูกเพิ่มเข้าไปในออปเจ็คModelเพื่อสามารถเข้าถึงได้ในหน้า View Template (ใช้ Thymeleaf)
@RequestMappingโดย default นั้น map ทุก HTTP reqeust เช่นGET,PUT,POSTถ้าเราจะเจาะจงว่าจะ map เฉพาะGETก็ทำได้เช่น@ReqeustMapping(method=GET)
ต่อมาที่ไฟล์ src/main/resources/templates/greeting.html ทำการเพิ่มโค๊ดด้านล่างลงไป
<!doctype html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <title>Getting Started : Serving Web Content</title> </head> <body> <p th:text="'Hello, ' + ${name} + '!'" /> </body></html>